Conditions Treated at MNC

Epilepsy was defined conceptually in 2005 as a disorder of the brain characterized by an enduring predisposition to generate epileptic seizures. This definition is usually practically applied as having two unprovoked seizures >24 h apart. The International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) accepted recommendations of a task force altering the practical definition for special circumstances that do not meet the two unprovoked seizures criteria. The task force proposed that epilepsy be considered to be a disease of the brain defined by any of the following conditions: (1) At least two unprovoked (or reflex) seizures occurring >24 h apart; (2) one unprovoked (or reflex) seizure and a probability of further seizures similar to the general recurrence risk (at least 60%) after two unprovoked seizures, occurring over the next 10 years; (3) diagnosis of an epilepsy syndrome.
Nearly everyone has had headache pain, and most of us have had it many times. A minor headache is little more than a nuisance that’s relieved by an over-the-counter pain reliever, some food or coffee, or a short rest. But if your headache is severe or unusual, you might worry about stroke, a tumor, or a blood clot. Fortunately, such problems are rare. Still, you should know when a headache needs urgent care and how to control the vast majority of headaches that are not threatening to your health.
Dementia is a term used to describe a group of symptoms affecting memory, thinking and social abilities severely enough to interfere with your daily life. It isn’t a specific disease, but several diseases can cause dementia.
Though dementia generally involves memory loss, memory loss has different causes. Having memory loss alone doesn’t mean you have dementia, although it’s often one of the early signs of the condition.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of a progressive dementia in older adults, but there are a number of other causes of dementia. Depending on the cause, some dementia symptoms might be reversible.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an unpredictable disease of the central nervous system that disrupts the flow of information within the brain, and between the brain and body.
The cause of MS is still unknown. Scientists believe that a combination of environmental and genetic factors contribute to the risk of developing MS.
The progress, severity and specific symptoms of MS in any one person cannot yet be predicted. Most people with MS are diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50, with at least two to three times more women than men being diagnosed with the disease.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine-producing (“dopaminergic”) neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra.
Symptoms generally develop slowly over years. The progression of symptoms is often a bit different from one person to another due to the diversity of the disease. People with PD may experience:
- Tremor, mainly at rest and described as pill rolling tremor in hands. Other forms of tremor are possible
- Bradykinesia
- Limb rigidity
- Gait and balance problems
The cause remains largely unknown. Although there is no cure, treatment options vary and include medications and surgery. While Parkinson’s itself is not fatal, disease complications can be serious. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) rated complications from PD as the 14th cause of death in the United States.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. The condition occurs when one of the major nerves to the hand — the median nerve — is squeezed or compressed as it travels through the wrist.
Sometimes it is hard to tell when a person is having a seizure. A person having a seizure may seem confused or look like they are staring at something that isn’t there. Other seizures can cause a person to fall, shake, and become unaware of what’s going on around them.
Learn about different types of seizures and their signs and symptoms so you can tell when someone is having a seizure.
Many older adults worry about their memory and other thinking abilities. For example, they might be concerned about taking longer than before to learn new things, or they may sometimes forget to pay a bill. These changes are usually signs of mild forgetfulness — often a normal part of aging — not serious memory problems.
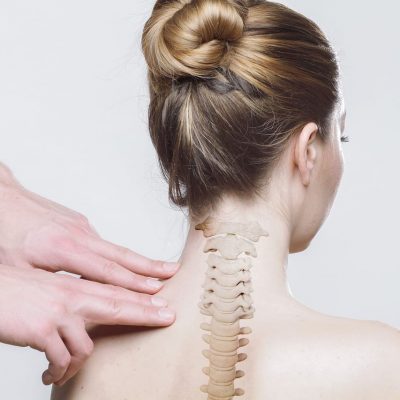
Back pain can range from a mild, dull, annoying ache, to persistent, severe, disabling pain. Pain in your back can restrict mobility and interfere with normal functioning and quality of life. You should always consult your health care provider if you have persistent pain.
Neck pain occurs in the area of the cervical vertebrae in your neck. Because of its location and range of motion, your neck is often left unprotected and subject to injury.
Pain in your back or neck area can be acute. That means it comes on suddenly and intensely. Chronic pain lasts for weeks, months, or even years. The pain can be continuous or intermittent.
Dizziness is a term used to describe a range of sensations, such as feeling faint, woozy, weak or unsteady. Dizziness that creates the false sense that you or your surroundings are spinning or moving is called vertigo.
Dizziness is one of the more common reasons adults visit their doctors. Frequent dizzy spells or constant dizziness can significantly affect your life. But dizziness rarely signals a life-threatening condition.
Treatment of dizziness depends on the cause and your symptoms. It’s usually effective, but the problem may recur.
TIAs are sometimes called mini-strokes, because their symptoms last only for a few minutes up to 24 hours before disappearing . But warning stroke is a better label, because a TIA often foreshadows a full-blown stroke and needs to be taken seriously.
TIAs are caused by a clot or blockage in the brain. The blockage is short term. The clot usually dissolves on its own or gets dislodged, and symptoms usually last for a short time.
A tremor is a rhythmic shaking movement in one or more parts of your body. It is involuntary, meaning that you cannot control it. This shaking happens because of muscle contractions.
A tremor is most often in your hands, but it could also affect your arms, head, vocal cords, trunk, and legs. It may come and go, or it may be constant. Tremor can happen on its own or be caused by another disorder.

Testing
The Michigan Neuroscience Clinic brings together the most experienced and qualified neurologists and specialists who work together to provide you with a coordinated and comprehensive care. We are the experts in our fields, thanks to our vast knowledge in the field of clinical care and research. We have the ability to create an environment where our experts can carry out their research and put the patients’ needs first. This results in better and improved quality of life for you.
Electromyography (EMG) measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerve’s stimulation of the muscle. The test is used to help detect neuromuscular abnormalities. During the test, one or more small needles (also called electrodes) are inserted through the skin into the muscle.
During the test, your nerve is stimulated, usually with electrode patches attached to your skin. Two electrodes are placed on the skin over your nerve. One electrode stimulates your nerve with a very mild electrical impulse. The other electrode records it. The resulting electrical activity is recorded by another electrode. This is repeated for each nerve being tested.
Videonystagmography (VNG) is a test that measures a type of involuntary eye movement called nystagmus. These movements can be slow or fast, steady or jerky. Nystagmus causes your eyes to move from side to side or up and down, or both. It happens when the brain gets conflicting messages from your eyes and the balance system in the inner ear. These conflicting messages can cause dizziness.
You can briefly get nystagmus when you move your head a certain way or look at some types of patterns. But if you get it when you don’t move your head or if it lasts a long time, it may mean you have a disorder of the vestibular system.
Your vestibular system includes organs, nerves, and structures that are in your inner ear. It is your body’s main center of balance. The vestibular system works together with your eyes, sense of touch, and brain. Your brain communicates with the different systems in your body to control your balance.
An EEG is a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain. During the procedure, electrodes consisting of small metal discs with thin wires are pasted onto your scalp. The electrodes detect tiny electrical charges that result from the activity of your brain cells. The charges are amplified and appear as a graph on a computer screen, or as a recording that may be printed out on paper. Your healthcare provider then interprets the reading.
Sensory evoked potentials studies measure electrical activity in the brain in response to stimulation of sight, sound, or touch. When the brain is stimulated by sight, sound, or touch, signals travel along the nerves to the brain. There, electrodes detect the signals and display them for your doctor to interpret.
Sensory evoked potentials studies involve 3 tests that measure response to visual, auditory, and electrical stimuli.
Sensory evoked potentials studies measure electrical activity in the brain in response to stimulation of sight, sound, or touch. When the brain is stimulated by sight, sound, or touch, signals travel along the nerves to the brain. There, electrodes detect the signals and display them for your doctor to interpret.
Sensory evoked potentials studies involve 3 tests that measure response to visual, auditory, and electrical stimuli.
Carotid (kuh-ROT-id) ultrasound is a safe, painless procedure that uses sound waves to examine the blood flow through the carotid arteries.
Your two carotid arteries are located on each side of your neck. They deliver blood from your heart to your brain.
Carotid ultrasound tests for blocked or narrowed carotid arteries, which can increase the risk of stroke. The results can help your doctor determine a treatment to lower your stroke risk.
An echocardiogram is a noninvasive (the skin is not pierced) procedure used to assess the heart’s function and structures. During the procedure, a transducer (like a microphone) sends out sound waves at a frequency too high to be heard. When the transducer is placed on the chest at certain locations and angles, the sound waves move through the skin and other body tissues to the heart tissues, where the waves bounce or “echo” off of the heart structures. These sound waves are sent to a computer that can create moving images of the heart walls and valves.
Procedures
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) provides palliation of seizure reduction for patients with medically refractory epilepsy. VNS is indicated for symptomatic localization-related epilepsy with multiple and bilateral independent foci, symptomatic generalized epilepsy with diffuse epileptogenic abnormalities, refractory idiopathic generalized epilepsy, failed intracranial epilepsy surgery, and other several reasons of contraindications to epilepsy surgery. Programing of the parameters is a principal part in VNS.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has become the treatment of choice for advanced stages of Parkinson’s disease, medically intractable essential tremor, and complicated segmental and generalized dystonia. In addition to accurate electrode placement in the target area, effective programming of DBS devices is considered the most important factor for the individual outcome after DBS.
Botox injections are noted primarily for the ability to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles. They’re also used to treat conditions such as neck spasms (cervical dystonia), excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), an overactive bladder and lazy eye. Botox injections may also help prevent chronic migraines.
Nerve blocks, or neural blockades, are procedures that can help prevent or manage many different types of pain. They are often injections of medicines that block pain from specific nerves. They can be used for pain relief as well as total loss of feeling if needed for surgery.
Perhaps the best-known nerve block is an epidural. Many pregnant women ask for an epidural during childbirth to ease the pain of labor and delivery. In an epidural, doctors inject an anesthetic drug into the space just outside the spinal column.
A trigger point injection can help soothe muscle pain, especially in your arms, legs, lower back and neck. It also can be used to treat fibromyalgia, tension headaches and myofascial pain.
Trigger points are painful “knots” in your muscles. They form when a muscle can’t relax. Sometimes you can feel these knots when you rub your muscle.
Injecting small amounts of anesthetic and steroid into the trigger point can help alleviate the pain.
Ultrasound-guided joint injections are a safe, non-invasive approach to treating pain, inflammation and impaired mobility. The procedure is often recommended when other conservative treatments such as oral medication, joint manipulation and physical therapy have been ineffective.
